Railway Recruitment Board(RRB) has announced vacancies for RRB JE and DMS. In Official notification branch wise syllabus is provided for RRB JE main CBT 2 examination. You can Download the main exam CBT 2 Branch Wise syllabus below here.
| Electrical Syllabus PDF Download | Mechanical Syllabus PDF Download | Civil Syllabus PDF Download | Electronic Syllabus PDF Download |
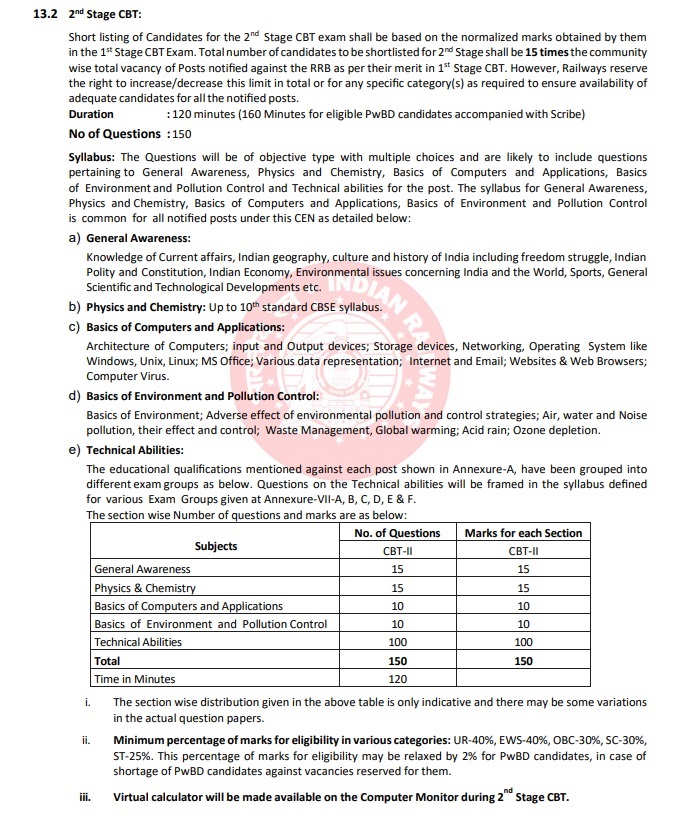
RRB JE CBT2 Exam Pattern
RRB JE CBT 2 exam will have 150 multiple-choice questions (MCQs) and each question will be 1 mark. The subjects included in the exam are General Awareness, Physics and Chemistry, Basics of Computers and Applications, Basics of Environment and Pollution Control, and Technical Abilities, To pass the exam, you need to score at least 40% marks. The exam duration is 2 hours (120 minutes). For each wrong answer, 1/3rd of a mark will be deducted as negative marking. Non-Technical section is common for all the branches.
RRB JE Syllabus for Electrical & Allied Engineering Exam Group– JE
| 1 Basic concepts: Concepts of resistance, inductance, capacitance, and various factors affecting them. Concepts of current, voltage, power, energy and their units. |
| 2 Circuit law: Kirchhoff‘s law, Simple Circuit solution using network theorems |
| 3 Magnetic Circuit: Concepts of flux, mmf, reluctance, Different kinds of magnetic materials, Magnetic calculations for conductors of different configuration e.g. straight, circular, solenoidal, etc. Electromagnetic induction, self and mutual induction. |
| 4 AC Fundamentals: Instantaneous, peak, R.M.S. and average values of alternating waves, Representation of sinusoidal wave form, simple series and parallel AC Circuits consisting of R.L. and C, Resonance, Tank Circuit. Poly Phase system – star and delta connection, 3 phase power, DC and sinusoidal response of R-Land R-C circuit. |
| 5 Measurement and measuring instruments: Measurement of power (1 phase and 3 phase, both active and reactive) and energy, 2 wattmeter method of 3 phase power measurement. Measurement of frequency and phase angle. Ammeter and voltmeter (both moving oil and moving iron type), extension of range wattmeter, Multimeters, Megger, Energy meter AC Bridges. Use of CRO, Signal Generator, CT, PT and their uses. Earth Fault detection |
| 6 Electrical Machines: (a) D.C. Machine – Construction, Basic Principles of D.C. motors and generators, their characteristics, speed control and starting of D.C. Motors. Method of braking motor, Losses and efficiency of D.C. Machines. (b) 1 phase and 3 phase transformers – Construction, Principles of operation, equivalent circuit, voltage regulation, O.C. and S.C. Tests, Losses and efficiency. Effect of voltage, frequency and wave form on losses. Parallel operation of 1 phase /3 phase transformers. Auto transformers. (c) 3 phase induction motors, rotating magnetic field, principle of operation, equivalent circuit, torque-speed characteristics, starting and speed control of 3 phase induction motors. Methods of braking, effect of voltage and frequency variation on torque speed characteristics, Fractional Kilowatt Motors and Single Phase Induction Motors: Characteristics and applications. |
| 7 Synchronous Machines: Generation of 3-phase e.m.f. armature reaction, voltage regulation, parallel operation of two alternators, synchronizing, control of active and reactive power. Starting and applications of synchronous motors. |
| 8 Generation, Transmission and Distribution: Different types of power stations, Load factor, diversity factor, demand factor, cost of generation, inter-connection of power stations. Power factor improvement, various types of tariffs, types of faults, short circuit current for symmetrical faults. Switchgears and Protection: Rating of circuit breakers, Principles of arc extinction by oil and air, H.R.C. Fuses, Protection against earth leakage / over current, etc. Buchholz relay, Merz-Price system of protection of generators & transformers, protection of feeders and bus bars. Lightning arresters, various transmission and distribution system, comparison of conductor materials, efficiency of different system. Cable – Different type of cables, cable rating and derating factor. |
| 9 Estimation and costing: Estimation of lighting scheme, electric installation of machines and relevant IE rules. Earthing practices and IE Rules. |
| 10 Utilization of Electrical Energy: Illumination, Electric heating, Electric welding, Electroplating, Electric drives and motors. |
| 11 Basic Electronics: Working of various electronic devices e.g. P N Junction diodes, Transistors (NPN and PNP type), BJT and JFET. Simple circuits using these devices |

